MIDI’s development has changed how we listen to electronic music today.
Earlier, a musician could not plug two instruments of different brands to make music.
But with MIDI, you can connect several of them to create music.
From notes to vibrato, the cables can carry all kinds of messages.
So, how can we use MIDI cables to their full potential?
Why do we need a MIDI interface? What are the benefits of MIDI? Where to custom MIDI Cable for your project?
We will learn everything about MIDI in the following article.

Chapter 1: About MIDI Cable
MIDI is a simple technique that helps you achieve many things in the music industry.
A MIDI cable connects two different musical components of different brands.
The MIDI cable can carry event messages, music data, vibrato, panning, and more. MIDI almost acts as a remote control for the music gear.
You can play a keyboard and change the sound module’s volume, pitch, and tempo.
A MIDI cable transfers the messages as data and not an audio signal.
Therefore, it offers more control over the other equipment.
A MIDI interface and MIDI controller are the end connectors of a MIDI cable.
The cables connect the device to the MIDI interface through a 5-pin connector type.
You need two of these cables per instrument to transmit and receive data.
A MIDI cable makes a musician’s job much more manageable.
MIDI is a technical standard that connects electronic musical instruments and computers.
It can be a communication protocol, a digital interface, or an electrical connector.
MIDI can connect various devices for playing, editing, and recording music.
Also, a single MIDI link can connect with sixteen channels through a MIDI cable.
Each of these channels connects a different set of instruments.
Earlier, electronic musical instruments from different manufacturers couldn’t communicate with each other.
However, a MIDI-compatible connector can connect modules, synthesizers, drum machines, etc.

Chapter 2: How does a MIDI cable work?
MIDI stands for Musical Instrument Digital Interface, and the device that creates these signals is the Master.
On the other hand, the device that receives the MIDI signals and responds accordingly to create a sound is known as a Slave.
All thanks to modern software, you can now create MIDI music on the computer as well, apart from the musical instrument.
The cable that connects the master device to the keyboard or any other instrument that reproduces sound is known as the MIDI cable.
Most devices have 1-3 MIDI port types, namely MIDI Out, MIDI In, & MIDI thru. Since MIDI is a one-way communication protocol, a single MIDI port will either transmit or receive MIDI data.
If you want to send MIDI signals from your keyboard to the computer, you must connect the MIDI Out jack of the keyboard to the MIDI In jack.
MIDI Through is named so because it allows only MIDI data to pass through it, unlike MIDI Out, which sometimes also carries other information.
Earlier, the MIDI Thru jack connected many MIDI devices to form a daisy chain, all contented to a common source.
This helped in building complex systems. To form this daisy chain, you must connect the MIDI Through of the first sound device to the MIDI In Port of the next one.
In all such examples, you will need a secondary cable that can transmit signals back and forth and not just in a single direction.
Chapter 3: Types of MIDI Cable
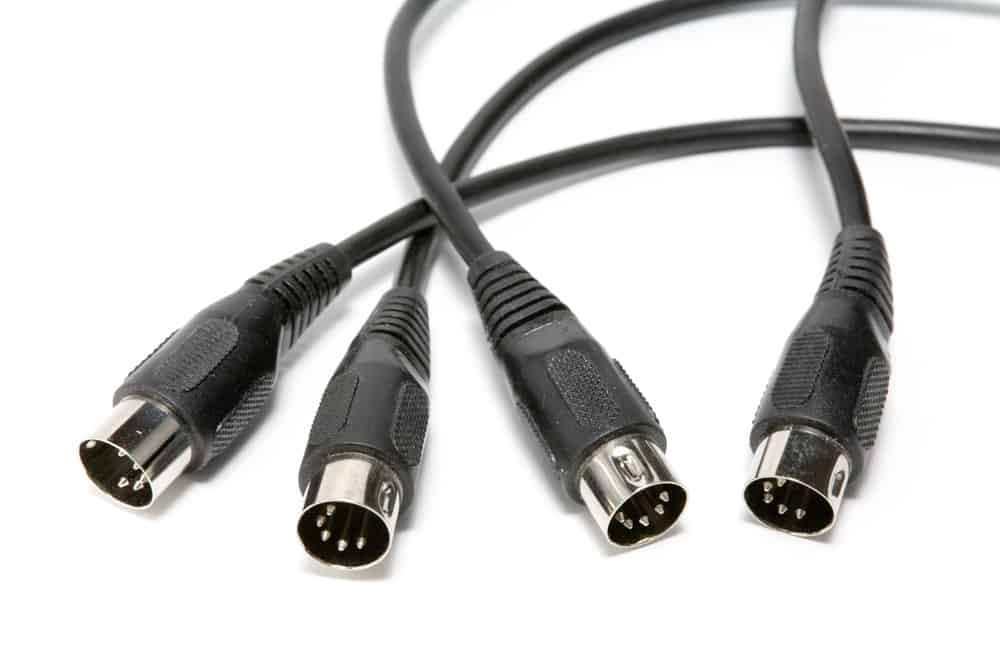

A MIDI cable can carry messages in various ways, i.e., through a 5-pin cable, USB, and more.
The transport speed determines the data a MIDI cable can carry and receive.
The types of MIDI cables are as follows:
USB cables connect the computer to other devices, including digital cameras and cell phones.
HD 15 Monitor Cable – It is the most common cable. It’s blue. It communicates the image data to the monitor processor.
USB and FireWire – The music industry requires computers a lot.
So, they need to be able to get the signals from an instrument as soon as possible.
Thus, a MIDI USB cable helps connects musical instruments to computers. It directly connects the host to the drivers, so you don’t need to configure it.
The MIDI cable usually has a USB port on one end and a 5-pin one on the other.
Bluetooth – Everything works through Bluetooth today.
Many software allows the use of Bluetooth. So the next time you use sound recording software, don’t forget to check it out.
Chapter 4: MIDI Cable – Which Connectors do You Use?
A MIDI connector is at the end of every cable that can send or receive a signal.
You can connect it to an audio device or a computer. It can be of the following types:
5-Pin MIDI DIN:
The 5-pin connector is one of the earliest MIDI connectors and the most common.
It’s slower than the other high-speed digital transports like USB and ethernet.
But it can manage communication speed effectively between two devices.
Thus, a 5-pin cable connects two MIDI devices without a computer.
USB and FireWire:
Computers have USB and FireWire ports that do not need any configuration.
It is, therefore, easier to connect a MIDI cable with a USB end between an instrument and a computer.
One end of this cable has a USB connector, while the other has the 5-pin one.
The best part about these connectors is that you must plug them in and play your instrument.
But you must install a driver on your PC to understand the information the MIDI cable sends.

TRS MIDI:
MIDI over TRA is a connection format that uses Tip, Ring and Sleeve as connectors. In form and functioning, it lies between the 5-pin Din and USB connectors.
Earlier, MIDI In/Out used traditional 5-Pin DIN connections, but as the hardware is becoming smaller daily, using DIN connections has become challenging.
Also, MIDI uses only three out of 5 pins of DIN, so adopting the Tip, ring and Sleeve format is not a problem.
You can usually witness this Tip, Ring and Sleeve pattern in 3.5mm phone jacks, but it is also used on pedals of electronic audio processors by some renowned manufacturers.
There are two types of TRS MIDI: Type A and Type B. The basic difference between these two is that Tip and Ring sleeves have been swapped.
So, if you connect a TRS cable between two MIDI devices having different types, it won’t work.
Both the MIDI types were popular before the MIDI Manufacturer’s Association or MMA officially standardized this format and released specifications for its use.
After publishing the MIDI 2.0 specification, Type A was put on priority. However, you will find both types in all the devices available in the market.
Some products, like Teenage Engineering Oplab Akai Force, use Type A, while the Novation Circuit, 1010 Black Box and others use Type B. Some devices use both, like ALm PEXP-2 and others.
When the two types are different, it seems difficult to make connections. However, most MIDI products come with a 5-PIn breakout adapter so that you can connect any of the two types without any extra adapters.
Even if you need one, Make Noise offers Type A adapters and 1010 Music offers Type B adapters.
Now, brands have started adhering to a single type across all their line of products. But, still, you may need adapters to pair devices together as new products are coming up in the market every day.
Undoubtedly, MIDI 2.0 is going to make successful prospects in the future. You will surely see this format venturing in different directions, and this is evident with the fact that mioXl and iConenctivity’s mioXl offer RTP MIDI for MIDI connections over Ethernet.
Also, with the surge of smartphones and smartphones as music-making tools, audio controllers with wi-fi and Bluetooth connectivity are making their presence in the market. Just wait for the endless interconnected possibilities in the future.
Chapter 5: MIDI In, MIDI Out, and MIDI Thru
A MIDI port can send or receive electronic data from instruments. Each MIDI port type serves a different purpose, and here’s what they do.
MIDI In – MIDI In receives data from another device. A sequencer or other hardware can send instructions on your gear, and MIDI In will receive them.
MIDI Out – MIDI Out transfers data from an audio device to another source.
For example, if you send some information from your synthesizer to outboard gear, you use MIDI Out. MIDI Out sends the information to the MIDI In of another gear.
MIDI Out is usually for the use of DAW or sequencer. The other instruments use MIDI in or MIDI Thru.
MIDI Thru – Whatever data comes from the MIDI In port, MIDI Thru duplicates it.
Thus, you can connect multiple devices without several ports on your sequencer.
Most of the devices come with MIDI Thru capabilities.
But if they don’t, you can use a MIDI splitter. It gives one the option of multiple ports that send the information with MIDI Thru.
Chapter 6: Benefits of MIDI Cable
A MIDI setup can offer much more than just recording your audio tracks. MIDI allows you to edit your sound and performance continually.
You don’t need to re-perform the part as well. From changing a piano sound to the chord progression, you can change anything on it.
The simplest MIDI loops can also turn into a multi-track studio in no time. MIDI can make every performance of yours better in the low time.
All you need is a computer and a MIDI controller. You can sequence, edit, and arrange your sound directly from the PC.
You can then create hundreds of tracks with different sounds for each.
Can also add a synthesizer to the mix to get the full analog sound.
Chapter 7: Custom MIDI Cable — How Can We Help?
If you’re looking for a way to set up your musical instruments, we can help you. We will help you find the right MIDI cable as per your needs.
We also customize the cables according to your needs easily.
You can then synthesize, edit, and produce your music. You can connect up to sixteen channels with your MIDI cable and produce music.
Can contact us for any information you may need about the MIDI cables.
Length of the MIDI cable:
The MIDI cable comprises a head and the length of the insulated wire. Though available in different lengths, MIDI cable with the most effective results should be 20 feet or less.
For long-distance connections (more than 20 feet), you need high-quality MIDI cables because low-quality cables do not guarantee the integrity of signals.
Types of MIDI cables:
There are different types of instruments and devices, and for them, different MIDI cables are available to make the connections possible and compatible.
As the musical instrument connects through MIDI, the cable has MIDI connectors at both its ends. However, computers do not have MIDI sound cards or MIDI in jacks.
So, if you want to connect your musical instrument to a computer or any other recording device, the cable should have at least one end with a USB or Firewire connector.
You can also use an adapter to change a MIDI connector to USB or Firewire.
MIDI couplers help you plug two MIDI cables into them, allowing extension of connection.
Alternatively, the transition from male MIDI to female one and vice versa is possible with MIDI splitters and Y-cables.
Some other types of MIDI cables include:
Colored MIDI cables
Braided MIDI cables
Bus-powered USB MIDI
Right-angled 5-pin MIDI cable and so on
Conclusion
A MIDI cable can make the life of any musician easier. It is a great way to connect different musical instruments.
You can also connect your connector to a computer and produce music anytime. The only issue with a 5-pin connector is that it sends the data slowly.
The LAN or Bluetooth connection prevents us from transmitting the right data.
If you need MIDI cables or any help, try our services. We can set up everything for you, giving you time to relax and make your music.


